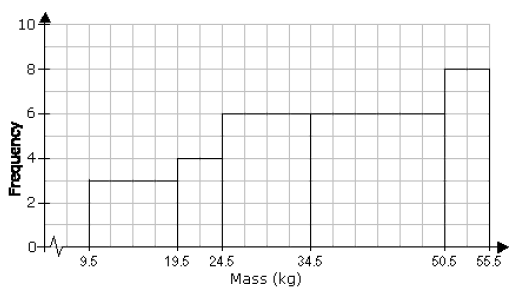
Class 9 Statistics: Mean, Median, Mode, Histogram, polygon, frequency polygon
Welcome to JSUNIL TUTORIAL's Class 9 Statistics: Mean, Median, Mode, and Graphical Representation of Data like Histogram, polygon, frequency polygon etc.
As a dedicated teacher, I'm here to help you excel in School Exams. Learn these essential statistical concepts with ease and boost your exam performance. Explore our expertly crafted sample papers and solved test papers to achieve that perfect score. Join me on this educational journey today
As a dedicated teacher, I'm here to help you excel in School Exams. Learn these essential statistical concepts with ease and boost your exam performance. Explore our expertly crafted sample papers and solved test papers to achieve that perfect score. Join me on this educational journey today